What is CLV (Customer Lifetime Value) – Free Calculator

In this article, we will take a look at the concept of Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) — a key metric that helps businesses understand the value each customer brings to their operations over the entire duration of their relationship. CLV is not only a measure of a customer’s past and present value but also a powerful forecasting tool that can inform strategic business decisions.
The Importance of CLV: Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is the total revenue a company can expect from a long-term relationship with a customer. Understanding CLV enables companies to allocate marketing resources more efficiently, improve profitability, and direct sales strategies effectively.
How to Calculate CLV
CLV can be calculated in two ways: a simpler method and a more advanced one. In its simplest form, CLV is calculated by multiplying the average revenue per customer by the average duration of the customer relation. This formula takes into account both the average revenue generated by the customer over a specific period and the length of the customer relation.
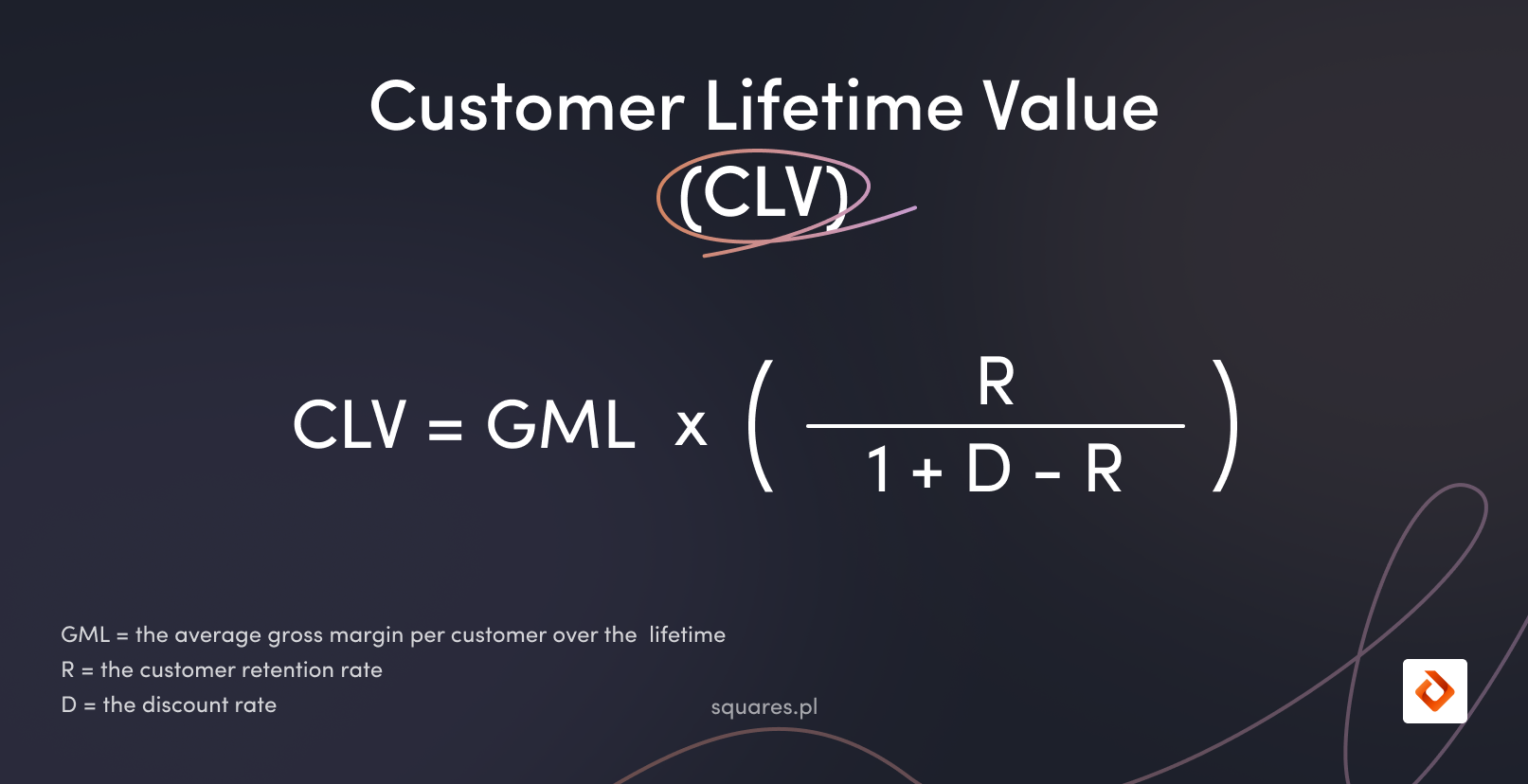
For subscription models, an expanded formula is often used where:
- GML is the average gross margin per customer over the customer’s lifetime
- R is the customer retention rate
- D is the discount rate
This formula allows for the inclusion of not only the revenues and costs associated with the customer but also the time value of money (using the discount rate) and the probability of retaining the customer over time (retention rate).
Using this formula is particularly useful for long-term customer relationships, where regular transactions or subscriptions form a significant part of the business model. With this formula, companies can more accurately forecast future revenues and better understand the value individual customers will bring to their business in the long run.
Where to Get Monthly Retention Rate (R)?
- Historical Data Analysis: The customer retention rate can be calculated based on the company’s historical data. This involves analyzing the number of customers at the beginning of a period (e.g., year) and comparing it with the number of customers who remained at the end of that period.
- Market Research: Surveys can be conducted to understand how long customers typically stay with a company. Customer surveys and return analysis can provide useful insights.
- Industry Benchmarks: In some cases, companies can also refer to industry standards or benchmarks for retention rates.
Where to Get Discount Rate (D)?
- Company’s Internal Rate of Return (IRR): The discount rate often corresponds to the company’s internal rate of return, which is a measure of the expected return on investment.
- Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC): The average cost of capital (WACC) can also be used, which takes into account the cost of both debt and equity.
- Risk Analysis and Market Inefficiencies: The discount rate should also reflect the risks associated with the company’s operations and market inefficiencies.
Examples of CLV Application
Example 1: Company A offers subscription services.
- Average Gross Margin per Customer (GML): 500 PLN per year.
- Customer Retention Rate (r): 80% (i.e., 0.8).
- Discount Rate (d): 10% (i.e., 0.1).

CLV is 1333.33 PLN. This means that the average value each customer brings to Company A over the entire duration of their relationship is 1333.33 PLN. This is the sum of the gross profit the company can expect from an average customer, taking into account the retention rate and discount rate.
A higher CLV indicates that customers are more valuable to the company over the long term. This allows Company A to better understand how much it can invest in acquiring and retaining customers while maintaining profitability.
Example 2: Company B sells products with long-term contracts.
- Average Gross Margin per Customer (GML): 300 PLN.
- Customer Retention Rate (r): 90% (0.9).
- Discount Rate (d): 5% (0.05).

In both cases, these calculations demonstrate how changes in the customer retention rate and discount rate affect the long-term value of the customer for the company. A higher retention rate and a lower discount rate increase the CLV, emphasizing the importance of customer retention and effective financial management.
Free CLV Calculator
Summary
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is a key metric in customer relationship management and strategic business planning. CLV allows companies to understand the total value a customer brings over the duration of their relationship with the company.
Key Points:
Understanding and utilizing CLV allows companies to allocate marketing resources more effectively, improve profitability, and better target sales strategies. It serves not only as a tool for assessing the current value of a customer but also for future forecasting.
- CLV can be calculated in two ways: a simple method (average revenue × average duration of the relationship) and an advanced method (considering gross profit margin, retention rate, and discount rate).
- The advanced CLV formula is: CLV = GML × (R / (1 + D – R)), where GML is the average gross profit margin, R is the retention rate, and D is the discount rate.
- The customer retention rate (R) can be determined based on historical data, market research, or industry benchmarks.
- The discount rate (D) is established based on the company’s internal rate of return, the average cost of capital, or risk analysis.
- Examples of CLV application demonstrate how different factors influence the long-term value of a customer for the company.
- A higher customer retention rate and a lower discount rate increase CLV.


